
Is the U.S. Dollar’s Unrivaled Legacy Hanging by a Thread?
In a surprising twist, the U.S. dollar’s historic reign as the world’s dominant reserve currency has slipped below the 60% mark for the first time in decades, as revealed in a groundbreaking report. While the U.S. dollar faces a slight dip, rival currencies such as the Euro, Pound, and Yen are beginning to witness a resurgence in global financial markets. This development comes at a time when a growing number of nations are taking steps to transact trade in their own national currencies, challenging the enduring supremacy of the greenback. This shift towards diversification away from the dollar has intensified significantly following the initiation of this idea by BRICS.
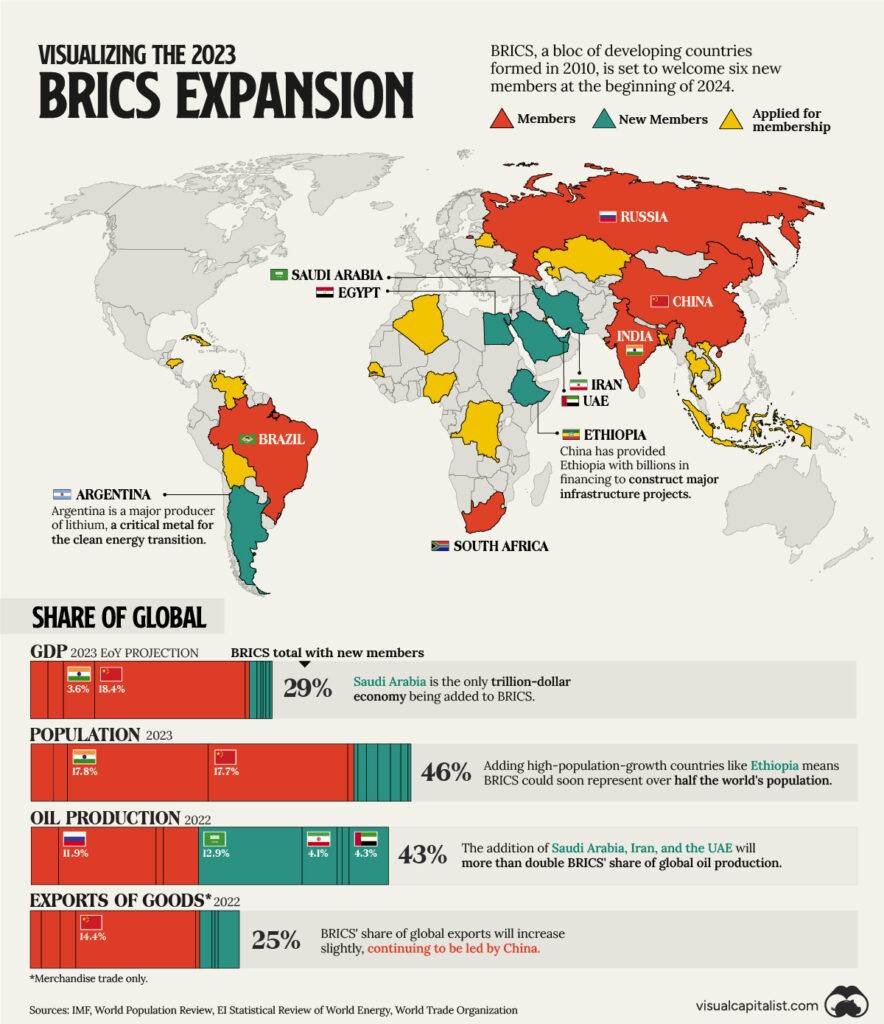
The BRICS consortium, comprised of Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa, is leading the charge to diminish the U.S. dollar’s dominance in the global reserve arena and replace it with a mosaic of local currencies. This strategic move is propelled, in part, by the White House’s stringent sanctions against developing nations, which have taken a toll on their economies and ignited a fervor within BRICS to seek alternatives to the U.S. dollar.
Even worse is the fact that many other countries have signed deals with BRICS, some of whom have been long term US allies like Saudi Arabia.
The Astonishing Plunge in Global Reserves for the U.S. Dollar
A look back reveals the astonishing journey of the U.S. dollar as the premier global reserve currency. In 2002, it accounted for a substantial 72% of global reserves, but over the last two decades, its share has witnessed a gradual but persistent decline. In the year 2023, the U.S. dollar’s stranglehold on global reserves has receded to 59%. In the span of 21 years, the greenback has relinquished 13% of its global market share, while other currencies are beginning to see a resurgence. Notably, the Chinese Yuan has made an impressive 3% gain within the same period and has the potential to surge further as more countries opt to settle trade in this currency.
Maria Zakharova, the Spokeswoman for Russia’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs, commented on these developments, stating, “The Euro’s share has now fallen to 19%, down from 28% in 2008. Moreover, the Yuan has surged to 3%, marking a remarkable threefold growth since 2016.” The BRICS alliance is actively encouraging other developing nations to reduce their reliance on the U.S. dollar and foster the use of local currencies in international trade. This growing trend indicates that many more countries are poised to distance themselves from the U.S. dollar, a move they believe will bolster their domestic economies.
BRICS vs. the U.S. Dollar: The Battle for Global Dominance
In a world dominated by the U.S. Dollar, a group of rising powers known as BRICS is challenging the preeminence of the American currency. With their combined economic might and ambition, these countries are seeking to reshape the global financial landscape. Join us as we delve into the high-stakes battle for global dominance. Buckle up, things are about to get interesting!
As BRICS puts increasing pressure on the U.S. dollar’s global dominance, the currency faces the risk of losing its footing as the world’s primary reserve currency. This shift would have significant implications, as it would leave the U.S. with limited means to fund its deficits and potentially compromise its global financial standing. The ongoing challenge to the dollar’s supremacy is a testament to the shifting dynamics of global finance and underscores the need for the U.S. to adapt to an evolving multipolar currency landscape.
Related: US Debt Skyrockets, Adds Half Trillion Dollars in 2 Weeks, Threatening American Prosperity
The Implications for the USA, Its People, and the Economy
The erosion of the U.S. dollar’s global dominance, as precipitated by the actions of BRICS and the ongoing trend of de-dollarization, could potentially have adverse consequences for the United States, its citizens, and its economy.
5 Risks or Challenges of the US Dollar Losing it’s Reserve World Currency Status
1. Economic Vulnerabilities: A diminished role for the U.S. dollar in global reserves may leave the country more exposed to economic vulnerabilities. The dollar’s status as the world’s primary reserve currency has allowed the U.S. to enjoy certain privileges, such as lower borrowing costs and a stable exchange rate. A shift away from the dollar could lead to increased volatility in financial markets and higher interest rates, potentially impacting American businesses and consumers alike.
2. Trade Deficits: The U.S. has historically run trade deficits, meaning it imports more than it exports. The dollar’s global dominance has helped sustain this pattern by providing a constant demand for the currency. If the dollar loses its reserve status, it may become more challenging for the U.S. to finance its trade imbalances, which could put pressure on the country’s balance of payments.
3. Inflation: A weaker dollar resulting from reduced global demand could contribute to higher inflation within the United States. A declining dollar often leads to rising import prices, which can translate into increased costs for American consumers and businesses. This, in turn, could impact the purchasing power of the average American citizen.
4. Geopolitical Influence: The U.S. dollar’s status as the world’s dominant reserve currency has also been a source of considerable geopolitical leverage for the United States. A shift away from the dollar could potentially diminish this influence, affecting the nation’s ability to shape global economic and political outcomes.
5. Fiscal Challenges: A decline in the dollar’s global standing may limit the U.S. government’s ability to finance its budget deficits through foreign purchases of U.S. debt. This could necessitate more significant domestic borrowing, potentially leading to higher interest rates and increased pressure on the national debt.
5 Potential Positive Aspects of the US Dollar Losing it’s Reserve World Currency Status
While there are potential challenges and risks associated with the loss of the U.S. dollar’s status as the world’s primary reserve currency, there are also some potential positive aspects to consider:
1. Export Competitiveness: A weaker U.S. dollar resulting from reduced global demand for it could make American goods and services more competitively priced in international markets. This could boost U.S. exports, potentially stimulating economic growth and creating jobs in export-oriented industries.
2. Reduced Trade Deficits: A shift away from the dollar as the dominant global reserve currency may encourage the U.S. to reduce its trade deficits. This could lead to a more balanced trade relationship with other nations, potentially strengthening the nation’s overall economic stability.
3. Diversification: A move toward a more diversified international monetary system could decrease the risk associated with relying heavily on a single currency. It could reduce the vulnerability of the U.S. economy to external shocks that could result from fluctuations in the value of the dollar.
4. Lower Costs for Foreign Borrowers: As the dollar’s dominance declines, foreign governments and entities may find it less expensive to borrow funds internationally, potentially stimulating global economic activity. This could indirectly benefit the U.S. economy if it leads to increased demand for American goods and services.
5. Economic Adaptation: Over time, the United States may adapt to a multipolar currency system by diversifying its own foreign currency holdings and investment strategies. Such adaptation could promote a more resilient and globally oriented financial sector.
It’s important to note that while these potential benefits exist, the process of the U.S. dollar losing its world currency status would likely be complex and involve both challenges and opportunities. The net impact on the U.S. economy would depend on various factors, including how effectively the U.S. government and private sector adapt to the changing global financial landscape.
In conclusion, while the shift away from the U.S. dollar as the world’s primary reserve currency may align with the aspirations of other nations and their pursuit of economic sovereignty, it also presents potential challenges and risks for the United States, its citizens, and its economy. Adapting to these changing dynamics will require careful consideration and strategic planning to ensure that the nation continues to prosper in an evolving global financial landscape.
Let us know which direction you’d prefer the US to go in the comments below.
