A study published in medRxiv by scientists from the National Institutes of Health and Moderna shows findings that mRNA vaccines actually hurt the long-term immunity to Covid after contracting infection compared to unvaccinated people.
The study published with medRxiv last month showed that a placebo-controlled vaccine group was compared to those who received the Moderna vaccine.
The research draws on data from Moderna’s 30,000-person clinical trial for its mRNA shots. It may help explain why so many Americans now suffer multiple Covid infections, sometimes within months.
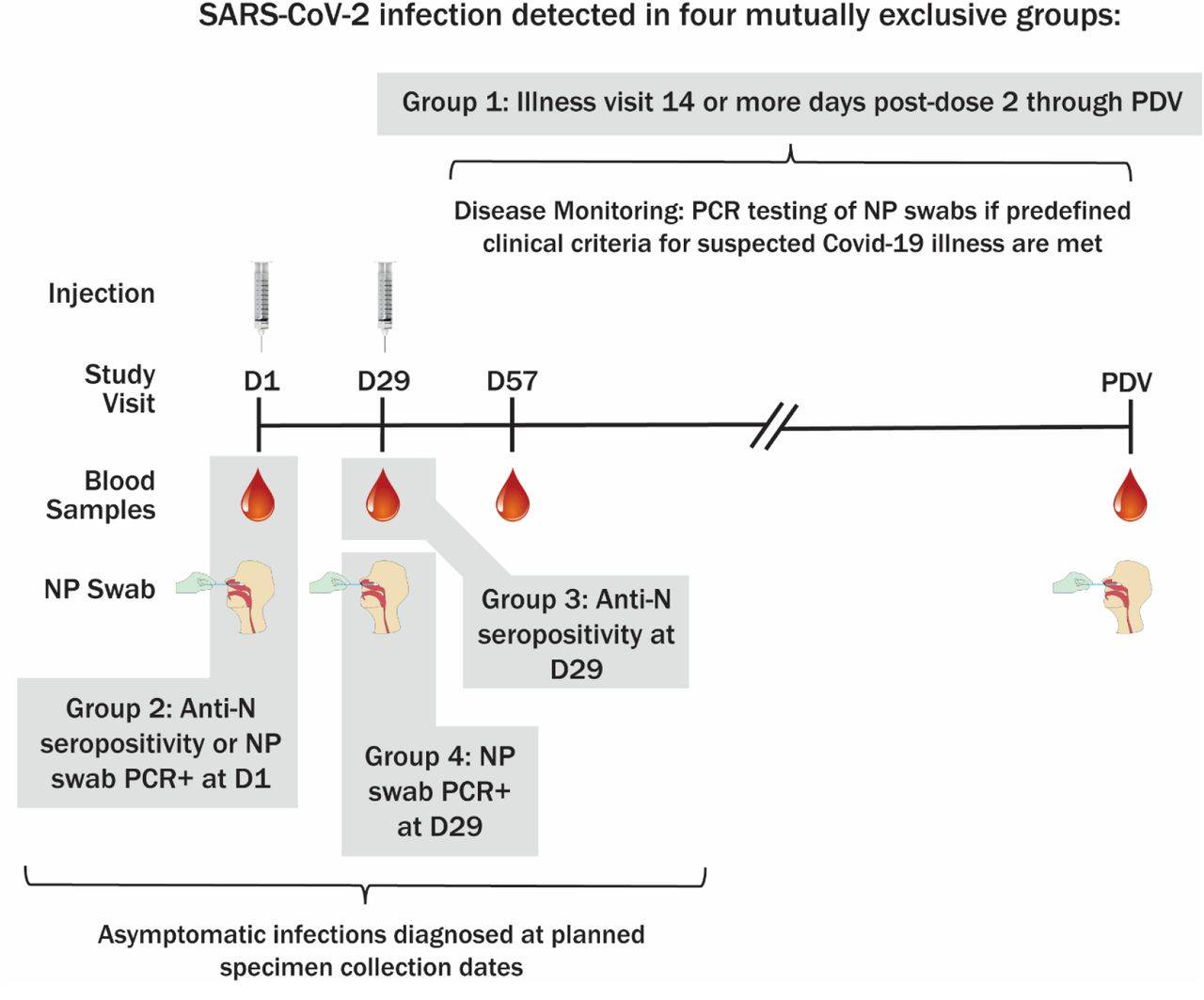
Question Does prior mRNA-1273 vaccination influence anti-nucleocapsid antibody seroconversion and/or seroreversion after SARS-CoV-2 infection?
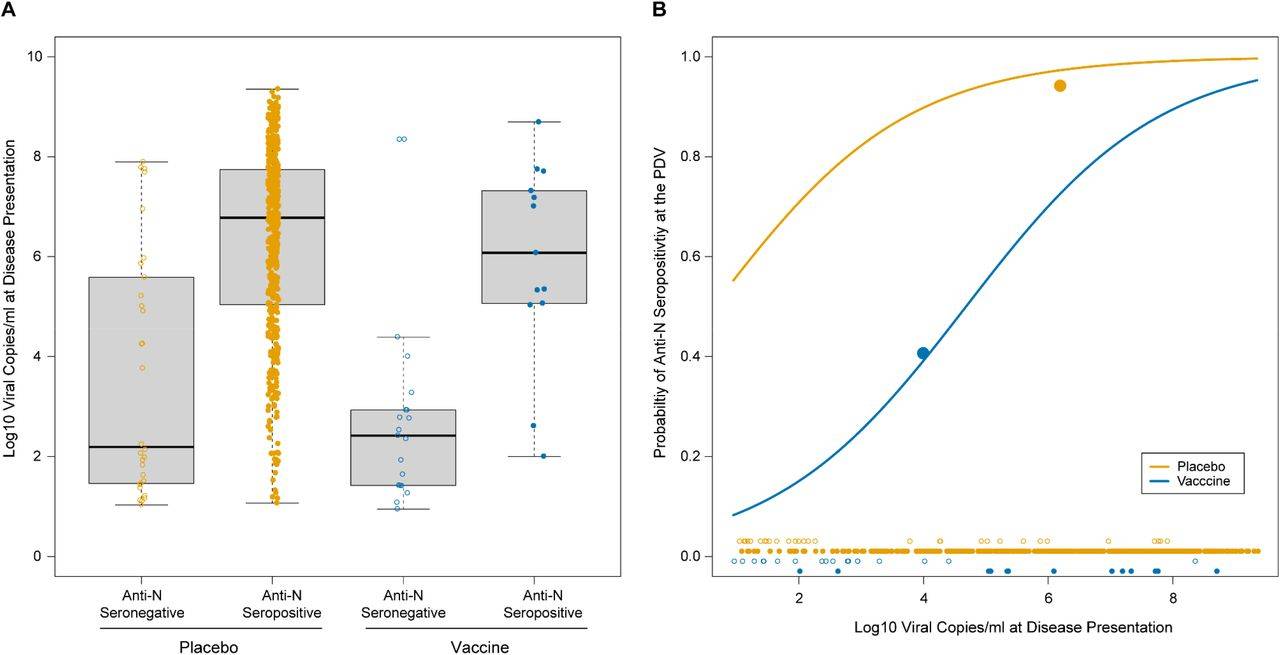
Findings Among participants in the mRNA-1273 vaccine efficacy trial with PCR-confirmed Covid-19, anti-nucleocapsid antibody seroconversion at the time of study unblinding (median 53 days post diagnosis and 149 days post enrollment) occurred in 40% of the mRNA-1273 vaccine recipients vs. 93% of the placebo recipients, a significant difference. Higher SARS-CoV-2 viral copy number upon diagnosis was associated with a greater chance of anti-nucleocapsid antibody seropositivity (odds ratio 1.90 per 1-log increase; 95% confidence interval 1.59, 2.28). All infections analyzed occurred prior to the circulation of delta and omicron viral variants.
Meaning Conclusions about the prevalence and incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection in vaccinated persons based on anti-nucleocapsid antibody assays need to be weighed in the context of these results.
“To evaluate for evidence of prior infection in a person with a history of COVID-19 vaccination, a test that specifically evaluates anti-N should be used. Past infection is best determined by serologic testing that indicates the presence of anti-N antibody,” according to the CDC.
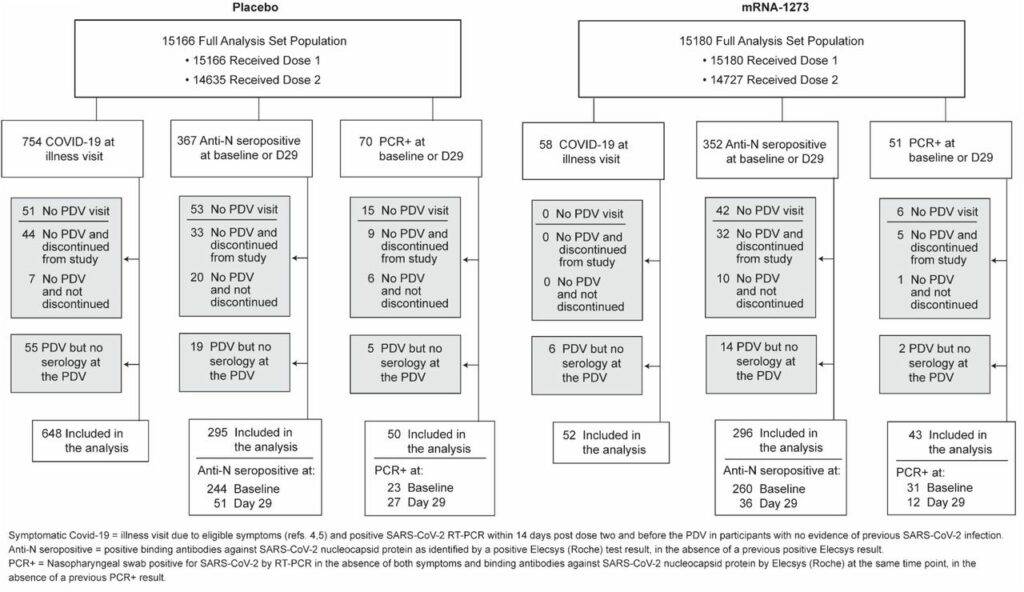
The study analyzed data from 1,789 participants (1,298 placebo recipients and 491 vaccine recipients) with Covid-19 infection at 99 sites in the US during the blinded phase (through March 2021).
The study concludes that anti-nucleocapsid antibody (anti-N Abs) may have lower sensitivity in patients vaccinated with Moderna who become infected. The study also mentioned that the anti-N Ab response in unvaccinated persons has been reported to be durable, with half-life estimates ranging from 68 to 283 days.
Among the participants with confirmed Covid-19 illness, only 21 out of 52 (40%) of people who received the Moderna shots had antibodies compared to the placebo recipients, 605 out 648 (93%).
Another NIH study was conducted over 5 months. The study followed vaccinated healthcare workers who were tested monthly. That study found that the antibody drops rapidly after one month after the second dose.
Those who advocate for the mRNA vaccine claim that a lack of nucleocapsid antibodies occurs because the shot helps people fight off Covid quickly and end up with lower viral loads.
This study essentially demolishes that theory.
Scientists from the National Institutes of Health and Moderna quietly posted the paper a month ago as a pre-print, but it has received little attention despite its import
Methods
We conducted a 5-month longitudinal prospective study involving vaccinated healthcare personnel, who were tested monthly for antibody titer, and sampled biweekly and on clinical indication for SARS-COV-2 polymerase chain reaction (PCR), to determine antibody decline and breakthrough infection.
Results
100 participants were recruited to the study. Antibody titer reached the climate after one month of the second dose of the vaccine, and declined rapidly thereafter: the median antibody levels were 895; 22,266; 9,682; 2,554 and 1,401 AU/ml in the day of the second dose, and in one month interval thereafter, respectively. In other words, four months after vaccination, the mean antibody level was 6% of the peak levels. During the study period, 4 breakthrough infections were diagnosed, 2 of which were asymptomatic, and the remaining two were mild cases; sharp elevation of antibody titer was seen after infection.
Conclusion
Antibody titer drops rapidly one month after the second dose of the vaccine. All infections within the study period were mild or asymptomatic, after which titer elevations were seen.